Key Vital Signs Monitor Based on MIMO Radar
Publication Details
Journal/Conference: International Conference on Smart Manufacturing
Authors: Michael Gottinger, Nicola Notari, Samuel Dutler, Samuel Kranz, Robin Vetsch, Tindaro Pittorino, Christoph Würsch, Guido Piai
DOI: 10.3390/s25134081
Key Vital Signs Monitor Based on MIMO Radar: A Revolutionary Approach to Contactless Health Monitoring
Paper Information:
- Title: Key Vital Signs Monitor Based on MIMO Radar
- DOI: 10.3390/s25134081
- Journal: Sensors
- Publication Date: June 30, 2025
- Authors: Michael Gottinger, Nicola Notari, Samuel Dutler, Samuel Kranz, Robin Vetsch, Tindaro Pittorino, Christoph Würsch, and Guido Piai
- Link: https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/25/13/4081
The Sleep Monitoring Challenge
Sleep apnea affects millions worldwide and is linked to serious health conditions including cardiovascular disease, cognitive impairment, stroke, and even sudden unexpected death. Traditional monitoring methods like polysomnography require multiple wired sensors attached to the body, creating an uncomfortable environment that can interfere with natural sleep patterns and require expensive manual evaluation by experts.
A Game-Changing Solution
This research introduces a compact 8 cm × 8 cm MIMO radar positioned next to the bed at approximately 1 meter distance, capable of providing a 3D point cloud for position estimation, sleep pose detection, and body part distinction. This represents a significant advancement over traditional single-channel continuous wave (CW) radar systems.
Key Technical Innovations
MIMO Radar System Specifications
The researchers used a sophisticated Vayyar IMAGEVK-74 MIMO system with impressive specifications:
- 20 transmit (TX) and 20 receive (RX) channels
- 60 GHz operating frequency with 5.2 GHz RF bandwidth
- Stepped-frequency continuous wave (SFCW) modulation
- 20 Hz measurement repetition rate
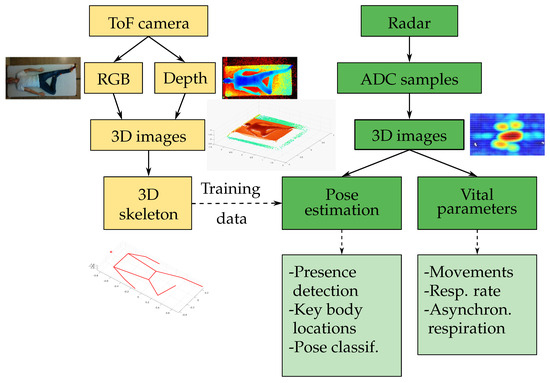
 Figure 1 | Overview of the main operations and functions with ToF camera data (yellow) and radar
data (green).
Figure 1 | Overview of the main operations and functions with ToF camera data (yellow) and radar
data (green).
AI-Powered Analysis
The system employs a convolutional neural network (CNN) trained using reference data from:
- Google MediaPipe Pose for 3D joint coordinate extraction
- Microsoft Azure Kinect DK time-of-flight camera for training data
- Inductive plethysmography belts for respiratory movement validation
Comprehensive Monitoring Capabilities
The MIMO radar system can detect and analyze:
-
Body Position and Pose Classification
- Supine, prone, and lateral sleeping positions
- Key skeletal joint localization (xiphoid, navel, shoulders, hips)
-
Vital Sign Monitoring
- Respiratory rate measurement
- Heart rate detection
- Breathing pattern analysis
-
Movement Detection
- Limb movements during sleep
- Periods of body motion identification
-
Advanced Respiratory Analysis
- Asynchronous chest-abdomen breathing detection
- Paradoxical breathing pattern recognition
- Phase difference analysis between chest and abdomen movements
Impressive Performance Results
The research team conducted extensive testing with 23 volunteers and achieved remarkable accuracy:
Position Accuracy
- Mean absolute error (MAE) < 5 cm for xiphoid and navel locations
- >90% of poses had errors smaller than 10 cm
- 90-95% categorical accuracy for pose classification
Breathing Rate Precision
- Supine position: 0.33 cycles/minute MAE
- Prone position: 0.06 cycles/minute MAE
- Lateral position: 0.80 cycles/minute MAE
Movement Detection
- 98.6% accuracy in detecting limb movements
- Successful identification of movements as small as 5 cm displacement
Clinical Applications and Future Potential
This technology offers significant advantages for:
- Home sleep apnea screening without uncomfortable sensors
- Long-term patient monitoring in healthcare facilities
- Privacy-preserving health surveillance (unlike video monitoring)
- Automated data evaluation reducing manual analysis costs
The system could potentially expand to include blood pressure monitoring and other cardiovascular measurements through advanced beamforming techniques.
Why This Matters
Unlike traditional radar systems that provide limited information due to destructive interference and lack of position data, this MIMO approach offers a practical compromise that minimizes complexity while achieving sufficiently high resolution for clinical applications.
The research represents a significant step toward contactless, automated health monitoring that could revolutionize how we approach sleep disorders, respiratory diseases, and vital sign monitoring in both clinical and home environments.
This breakthrough technology combines the precision of advanced radar imaging with AI-powered analysis, offering a glimpse into the future of non-invasive health monitoring where patient comfort and clinical accuracy can coexist seamlessly.